MRCS, UK is a tailored training programme exclusively for the medical aspirants looking for a career in surgical department. MRCS training hospitals in India gives a tremendous exposure to the medical aspirants to become a world class surgeon with exposure in various fields of surgery. The MRCS examination is a decisive milestone in a surgical career; it determines whether a surgical trainee possesses the applied knowledge, skills and attributes to complete basic training. MRCS training hospitals in Kerala and MRCS training hospitals in India will be the best options for medical aspirants looking to progress to next level of professionalism and looking for best PG courses after MBBS and courses after MBBS without NEET PG. The successful MRCS surgeons working in more than 100 countries including India, Pakistan, Saudi Arabia, the UAE and many more.
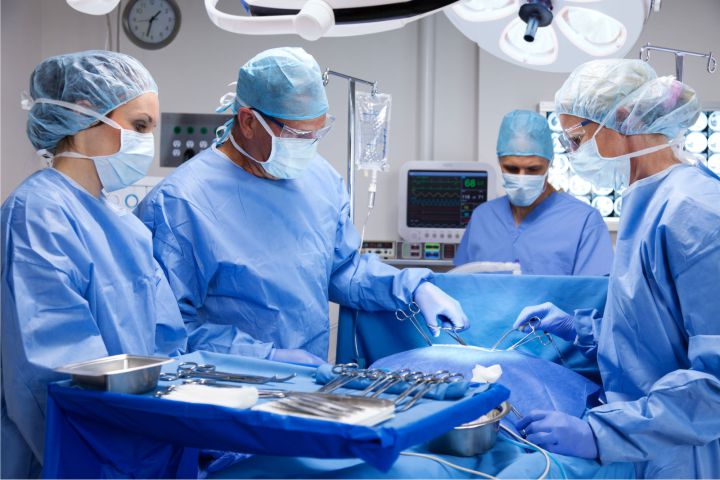
To enhance the scope of the core clinical training, we have partnered with the top MRCS training hospitals in India. The candidates will be benefitted by the bedside teaching, exposure towards various surgical departments with regular assessments in these MRCS training hospitals in India. The dedicated mentors and consultants of the MRCS training hospitals in India will provide continuous support throughout the programme. Candidates will be posted in relevant departments as post graduate trainees in our associated MRCS training hospitals in India. The training at these hospitals is conducted by faculty with profound experience in teaching and practice. As we have partnered with MRCS training hospitals in India in various states including Tamil Nādu, Kerala, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, and Gujarat, the candidates gets an option to choose a preferred location. The extensive clinical experience gained at these hospitals will give immense exposure to the candidates to work in India and UK.
Surgeons are the most demanding professionals across the globe. Moreover, Indian surgeons are respected the most. A MRCS certified surgeon receives a global recognition and wider benefits including international opportunities and better remuneration. Further after completing the speciality training levels in UK, the doctors and surgeons can apply for a Certificate of Completion of Training (CCT) which is highly recognized in Indian Hospitals and Universities. After passing the MRCS (UK), doctors can practice surgery in many countries except USA and Canada without any licensing examinations.
I.Applied Basic Science
No. of Questions: 180 questions (MCQ and EMQ)
Duration: 3 hours
II.Principles of Surgery in General
No. of Questions: 120 questions (MCQ and EMQ)
Duration: 2hrs
For details regarding Exam dates, eligibility, fees, exam centers, etc. kindly visit the MRCS website
Part A : https://www.rcseng.ac.uk/education-and-exams/exams/search/intercollegiate-mrcs-part-a/
OSCE : https://www.rcseng.ac.uk/education-and-exams/exams/search/intercollegiate-mrcs-part-b-osce/
| S.NO | Department |
|---|---|
| 1 | Urology |
| 2 | ENT / Head and Neck Surgery |
| 3 | General Surgery |
| 4 | Plastic Surgery and Burns |
| 5 | Neurosurgery | 6 | Cardiothoracic Surgery |
| 7 | Paediatric Surgery |
| 8 | Accident and Emergency |
| 9 | Orthopedics and Trauma |
Yes, MRCS (Membership of the Royal College of Surgeons) is increasingly seen as a viable alternative to MS (General Surgery) in India, especially for doctors aiming for international surgical careers or specialized surgical training abroad. While MS is a nationally recognized postgraduate qualification, MRCS is a globally respected postgraduate membership that demonstrates core surgical competencies and is required for higher surgical training in the UK and many other countries.
For Indian doctors, MRCS provides an edge in global job markets, particularly in the UK, Middle East, Ireland, Singapore, and more.
Many doctors pursue MRCS as part of broader PG courses after MBBS, especially those interested in bypassing competitive NEET-PG routes or targeting international pathways. Now, IMSTP provides MRCS training hospitals in India that offers structured preparatory programmes, clinical rotations, and mentorship to help doctors prepare for MRCS Part A and Part B (OSCE).
Thus, for MBBS graduates seeking a globally mobile surgical career and an alternative to conventional PG routes, MRCS is a highly valuable option—provided they plan their training pathway carefully and align it with their long-term goals.
You can appear for MRCS (Part A) directly after completing your MBBS, as there is no mandatory surgical experience required to register for the exam. However, having proper structured clinical training in surgical practice can significantly enhance your understanding and preparation, especially for Part B (OSCE). Many Indian doctors choose MRCS as part of their career pathway when exploring courses after MBBS without NEET PG, especially if they’re aiming for international opportunities. Several MRCS training hospitals and institutions in India offer structured preparatory courses, clinical skills workshops, and mock OSCEs that simulate the UK exam format. These programs help bridge the clinical experience gap and prepare candidates comprehensively for the examination.
The best time to start preparing for the MRCS (Membership of the Royal College of Surgeons) exam largely depends on your career goals and level of clinical exposure. Ideally, beginning MRCS preparation after MBBS offers the right balance of time, focus, and flexibility. At this stage, candidates can fully concentrate on the theoretical aspects of MRCS Part A, and enroll in structured MRCS training programs offered by reputed hospitals, which provide exposure to surgical departments and academic support. Starting during internship is possible for highly motivated individuals but can be challenging due to time constraints and limited surgical experience. On the other hand, preparing for MRCS after completing a postgraduate degree like MS or DNB in Surgery provides a strong clinical foundation for MRCS Part B (OSCE) but may require revisiting basic sciences for Part A. For those exploring alternatives, other PG courses after MBBS include MS, DNB, or super-specialty options in India, as well as international pathways like USMLE (USA), PLAB or MRCS (UK), or surgical residencies in Australia and Germany. Overall, starting MRCS preparation soon after MBBS is considered the most effective route for those aspiring for international surgical training.
Yes, there are several MRCS training centres and coaching programs available in India to support candidates preparing for the MRCS exams. These programs offer structured guidance, mock exams, eportfolio preparations, and clinical exposure to help candidates succeed in both Part A and Part B (OSCE). Many reputed hospitals function as MRCS training hospitals in India, providing hands-on experience and academic mentorship. These centres often collaborate with UK-based training bodies or offer preparatory courses aligned with the MRCS curriculum. These pathways offer opportunities for international exposure, hospital-based training, and career advancement without going through the Indian PG entrance route.
If you’re planning to work as a surgeon in the UK, having the MRCS (Membership of the Royal College of Surgeons) qualification can be a significant advantage—and in most cases, you do not need to take PLAB. The MRCS is accepted by the General Medical Council (GMC) as proof of postgraduate medical competence, which means MBBS graduates who clear both Part A and Part B of the MRCS exam can directly apply for GMC registration without going through the PLAB route. This makes MRCS not just a career-enhancing credential, but also a direct alternative to PLAB for those focused on surgical roles in the NHS. For medical graduates exploring further academic and clinical options, PG courses after MBBS extend far beyond traditional NEET PG-based pathways. Many students now choose the MRCS route specifically because it opens doors to surgical training abroad while also allowing access to MRCS training hospitals in India, where structured guidance and hands-on experience help build a strong foundation for a surgical career.
Yes, MRCS exams are conducted in India, and candidates do not necessarily need to travel abroad to take them. The MRCS Part A (written exam) is held multiple times a year at various test centers in major cities such as Delhi, Mumbai, Chennai, Hyderabad, and Bangalore. However, test center slots are limited and allocated based on availability, so it is important to register early to secure a preferred location. The MRCS Part B (OSCE) is also conducted in India at select centers, though the number of seats is even more restricted, and booking is on a first-come, first-served basis. To support exam preparation, several reputed MRCS training hospitals in India offer comprehensive training programs. These centers provide clinical exposure, academic support, and mock exams designed to simulate the actual MRCS assessment, helping candidates build the knowledge and practical skills required to succeed.
The overall cost for Indian candidates pursuing MRCS includes exam fees, training, and optional clinical exposure. The MRCS Part A exam typically costs around £600–£700, while Part B (OSCE) is priced between £1,000–£1,200, depending on the exchange rate and test center. In addition to exam fees, many candidates choose to enroll in structured clinical training programs offered through recognized MRCS training hospitals, where the clinical training fee ranges from ₹15 to ₹20 lakhs for a 2-year period. These programs often include hands-on experience, surgical rotations, academic mentorship, and mock assessments, providing a strong foundation for both the exams and future surgical practice. While this may seem like a significant investment, it is generally more cost-effective than pursuing MD/MS programs in India, which can cost significantly more in private institutions and also require clearing competitive entrance exams. For MBBS graduates considering their next step, MRCS presents an internationally recognized alternative to traditional PG courses after MBBS, offering both global mobility and specialized surgical training within a streamlined and professionally guided framework.
The MRCS, UK while not officially recognized as an MD/MS equivalent by the National Medical Commission (NMC) in India, holds significant value for Indian doctors—especially those seeking international surgical careers. It is a highly respected and globally acknowledged qualification that opens doors to GMC registration in the UK, eligibility for Core Surgical Training, and potential employment in NHS hospitals. For Indian MBBS graduates, MRCS serves as a strong and structured alternative to traditional PG courses after MBBS, offering clinical credibility, academic growth, and global mobility.
Although it may not be listed as a formal postgraduate degree by the NMC, Indian doctors with MRCS are increasingly being valued in private hospitals, academic collaborations, and international training programs. Many reputed MRCS training hospitals in India provide high-quality surgical exposure and exam preparation, helping candidates gain the skills needed to compete globally. In essence, while MRCS may not replace an MD/MS for certain regulatory or academic roles within India, it greatly enhances the professional profile of Indian doctors and paves the way for exciting career opportunities abroad.
You can pursue MRCS while working full-time in a hospital in India, and this is a common pathway for many Indian doctors aiming for an international surgical career. To make the most of your preparation, it’s important that you are working in a surgical unit or as a surgical trainee, as this provides day-to-day clinical exposure relevant to the MRCS curriculum. This experience is crucial not only for understanding applied surgical knowledge but also for gaining the practical skills assessed in MRCS Part B (OSCE). But it can be challenging and requires disciplined time management and strong motivation. The workload of a full-time surgical job, especially in busy clinical settings, often leaves limited time for structured study.
It’s also important to maintain an e-portfolio, which involves regularly documenting clinical experiences, procedural logs, reflective practice, and professional development. This can be time-consuming when balancing hospital duties, but it is a key requirement for demonstrating surgical competence, especially for those aiming to enter Core Surgical Training (CST) in the UK.
Doctors training through MRCS training hospitals in India often have the advantage of a more exam-oriented environment, but unlike structured residency programs, there are fewer formal academic sessions. Compared to traditional PG courses after MBBS like MS or DNB, MRCS preparation while working can be less predictable, but it provides a direct path to international surgical careers for those who can manage both clinical responsibilities and focused self-study.
After clearing MRCS, Indian doctors become eligible for a range of job opportunities in the UK, particularly within the NHS (National Health Service). The most immediate advantage is eligibility to apply for GMC (General Medical Council) registration, which is a prerequisite to practice medicine in the UK. Once registered, MRCS-qualified doctors can apply for roles such as Core Surgical Trainees (CST), Trust Grade Doctors, or Clinical Fellows in surgical specialties like general surgery, trauma and orthopaedics, ENT, or urology.
These roles not only offer hands-on surgical experience but also serve as a stepping stone to competitive higher surgical training positions in the UK. Compared to those taking other PG courses after MBBS, MRCS holders are particularly well-positioned for surgical career progression because the qualification is aligned with UK training standards. Many candidates who train at MRCS training hospitals in India gain relevant clinical experience and prepare their e-portfolio, making their transition into the UK system smoother and more competitive.
To apply for surgical training posts in the UK with MRCS from India, the first step is obtaining GMC (General Medical Council) registration. Once you’ve successfully cleared MRCS Part A and Part B, you become eligible to apply for GMC registration, which also requires your MBBS degree, internship completion proof, and English language proficiency (IELTS/OET). After securing GMC registration, you can begin applying for surgical positions such as Core Surgical Training (CST), Trust Grade posts, or Clinical Fellow roles through platforms like NHS Jobs and Oriel.
This process can seem complex, especially for those unfamiliar with the UK healthcare system. That’s why IMSTP Educational Services provides end-to-end guidance—including personalized support for GMC registration, documentation review, and applying for NHS jobs. With the clinical exposure gained through MRCS training hospitals in India and a properly maintained e-portfolio, Indian doctors are well-positioned to compete for these posts. Compared to traditional PG courses after MBBS, this pathway offers a globally recognized surgical career without NEET PG and with strong long-term prospects in the UK healthcare system.
Securing a surgical training position in the UK after clearing MRCS is definitely competitive, but it is an achievable and rewarding goal for well-prepared candidates. The MRCS qualification is highly respected and serves as a strong foundation for applying to Core Surgical Training (CST) posts. Indian doctors who gain clinical experience in reputed MRCS training hospitals in India and maintain a robust e-portfolio showcasing audits, teaching, leadership, and reflective practice stand out in the selection process.
Compared to traditional PG courses after MBBS, MRCS offers a direct and internationally recognized pathway that UK employers value greatly.
Beyond the UK, MRCS holders also enjoy excellent opportunities in the GCC countries—such as UAE, Saudi Arabia, and Qatar, where there is a growing demand for skilled surgeons with internationally recognized qualifications and value the MRCS credential when recruiting surgeons and specialists. Similarly, several ASEAN countries like Singapore, Malaysia, and Thailand recognize MRCS, offering rewarding clinical and teaching positions.
Yes, the MRCS qualification greatly supports your long-term career growth and is especially valuable when applying for fellowships or senior surgical roles in Gulf and other Western countries. While MRCS alone may not guarantee immediate appointment to senior roles when applying directly from India, it significantly strengthens your profile.
In the Gulf region—including countries like the UAE, Saudi Arabia, Oman, and Qatar—Indian doctors are typically required to clear a licensing exam such as DHA (Dubai Health Authority), HAAD, or MOH to begin clinical practice. Initially, you may be appointed as a general practitioner or medical officer. However, once you gain local experience, the MRCS qualification is highly regarded for promotions to specialist or senior registrar roles in surgery, especially in government and private tertiary hospitals.
You can apply for MRCS Part B (OSCE) without formal surgical training, but it is strongly recommended to have structured clinical or surgical experience before attempting it. Unlike Part A, which is theory-based and can be cleared with self-study, Part B is a practical, skills-based exam that assesses communication, clinical judgment, operative knowledge, and procedural skills across multiple stations.
Without formal surgical training or hospital-based exposure, especially in areas like surgical anatomy, instrument handling, and patient interaction, many candidates find the OSCE challenging. That’s why many doctors in India choose to undergo hands-on mentorship or rotations at recognized MRCS training hospitals, even if they haven’t pursued a full-time PG course.
For Indian MBBS graduates who haven’t gone through MS or DNB, MRCS offers a route into surgery through an internationally benchmarked pathway—one of the most viable PG courses after MBBS without NEET PG. However, it’s advisable to gain at least 6–12 months of practical surgical experience or attend focused OSCE coaching workshops to build confidence before sitting for Part B.
Yes, a growing number of Indian doctors have successfully pursued MRCS and built impressive careers in the UK, Middle East, and India. Their success reflects the increasing recognition of MRCS as a credible and structured pathway in surgery, especially for those who prefer an internationally aligned alternative to traditional PG courses after MBBS.
Many of these doctors began their journey with hands-on clinical exposure in MRCS training hospitals in India, followed by disciplined preparation for Part A and Part B exams. Their achievements demonstrate that with focused training, strong clinical foundations, and portfolio-building, Indian doctors can clear the MRCS exams and progress toward specialist roles both in India’s private sector and globally.
The growing number of Indian MRCS holders also highlights how the qualification is becoming a trusted benchmark for surgical competency, opening doors to opportunities that were once accessible only through MS or DNB.

Copyright © 2024
WhatsApp us